Grenoble: Industry, Training, Research in synergy
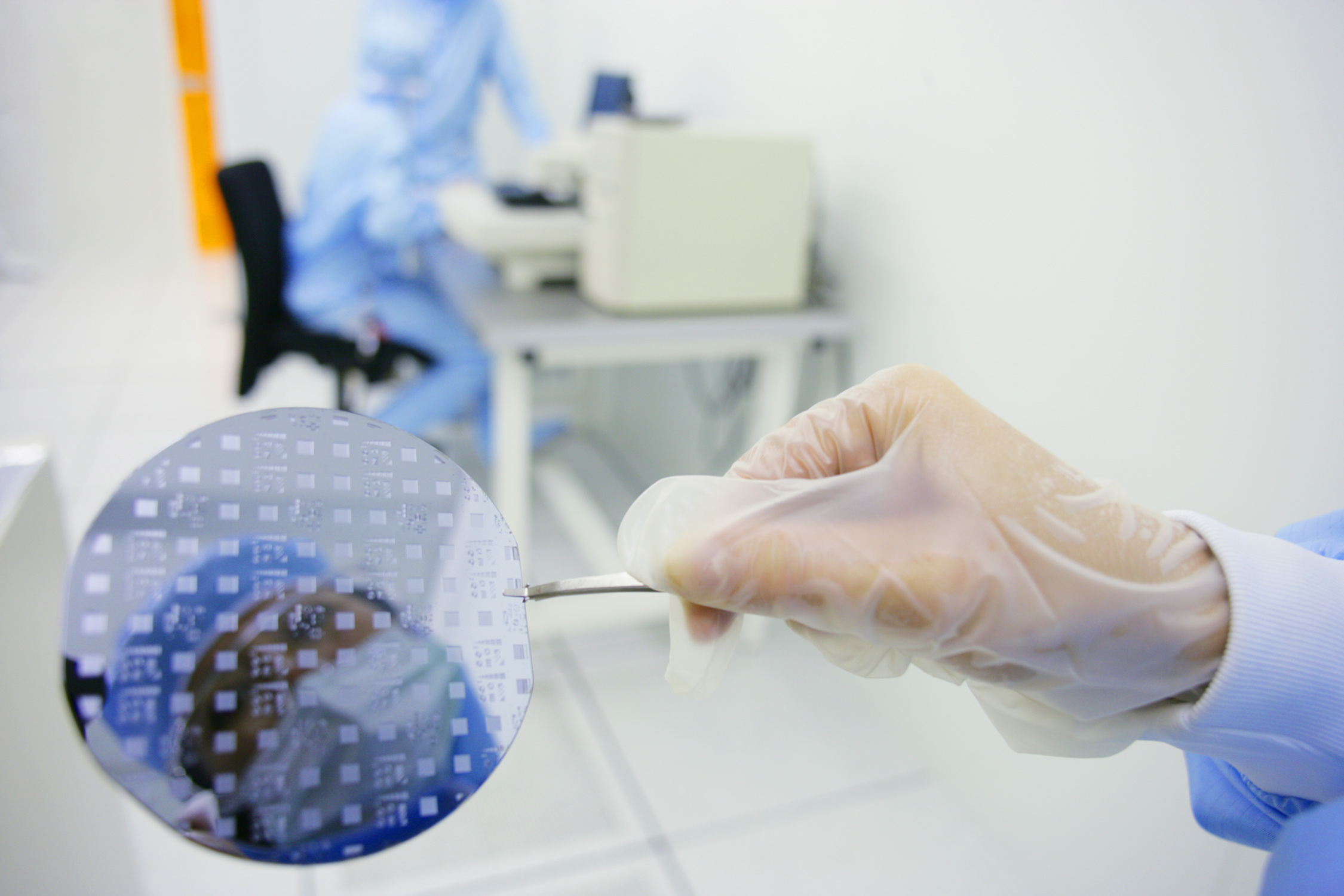
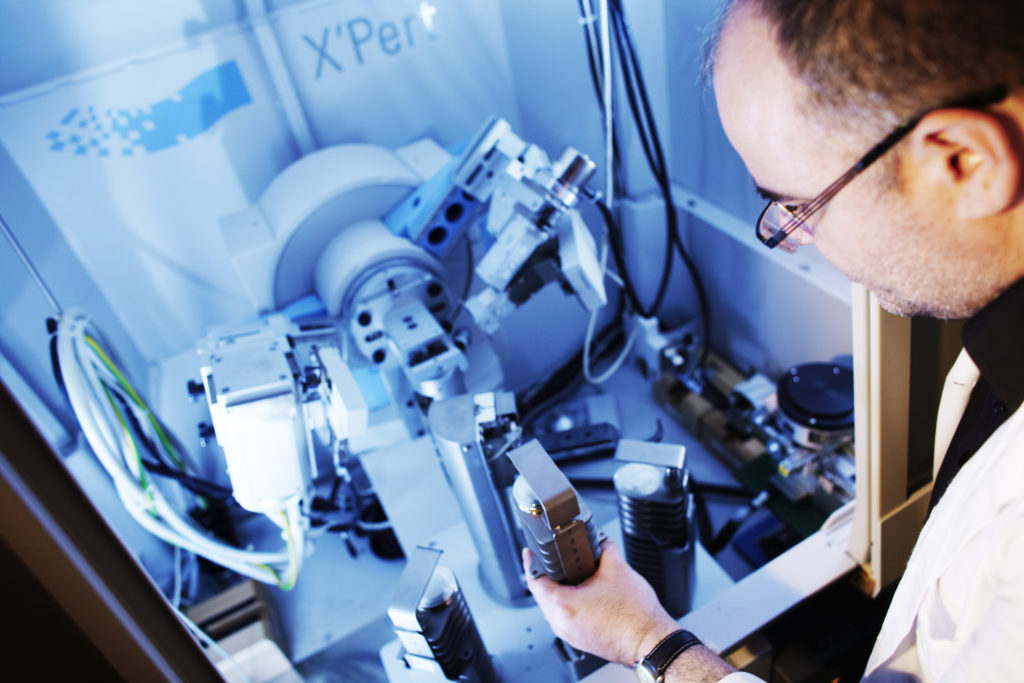


Grenoble INP – Phelma, UGA
is supported by:
- Largeresearch organisations: CNRS, CEA, INRIA, INSERM.
- 200 laboratories created by universities in the region.
- Lecturers and researchers from the school are present at 10 of these laboratories.
- “Large Instruments”: ESRF, ILL, European Molecular Biology Laboratory – EMBL, Institut de Biologie Structurale (Institute of Structural Biology) – IBS, Laboratoire National des Champs Magnetiques Intenses (National Laboratory for High Magnetic Fields) – LNCMI

Grenoble INP – Phelma, UGA
is supported by:
- Largeresearch organisations: CNRS, CEA, INRIA, INSERM.
- 200 laboratories created by universities in the region.
- Lecturers and researchers from the school are present at 10 of these laboratories
- “Large Instruments”: ESRF, ILL, European Molecular Biology Laboratory – EMBL, Institut de Biologie Structurale (Institute of Structural Biology) – IBS, Laboratoire National des Champs Magnetiques Intenses (National Laboratory for High Magnetic Fields) – LNCMI
Inspire innovation!
The school benefits from the exceptional high-tech environment of the 250 hectares of the Presqu’île de Grenoble. The MINATEC (micro- and nanotechnologies) and GIANT(Grenoble Innovation for Advanced New Technologies) innovation campuses give it strong connections with research teams and industrial partners (startups, companies). A French-styleMIT to meet the major challenges facing society: Information and communication technologies, renewable energy and environmental issues, biosciences and health.
Inspire innovation!
The school benefits from the exceptional high-tech environment of the 250 hectares of the Presqu’île de Grenoble. The MINATEC (micro- and nanotechnologies) and GIANT(Grenoble Innovation for Advanced New Technologies) innovation campuses give it strong connections with research teams and industrial partners (startups, companies). A French-styleMIT to meet the major challenges facing society: Information and communication technologies, renewable energy and environmental issues, biosciences and health.